Blog
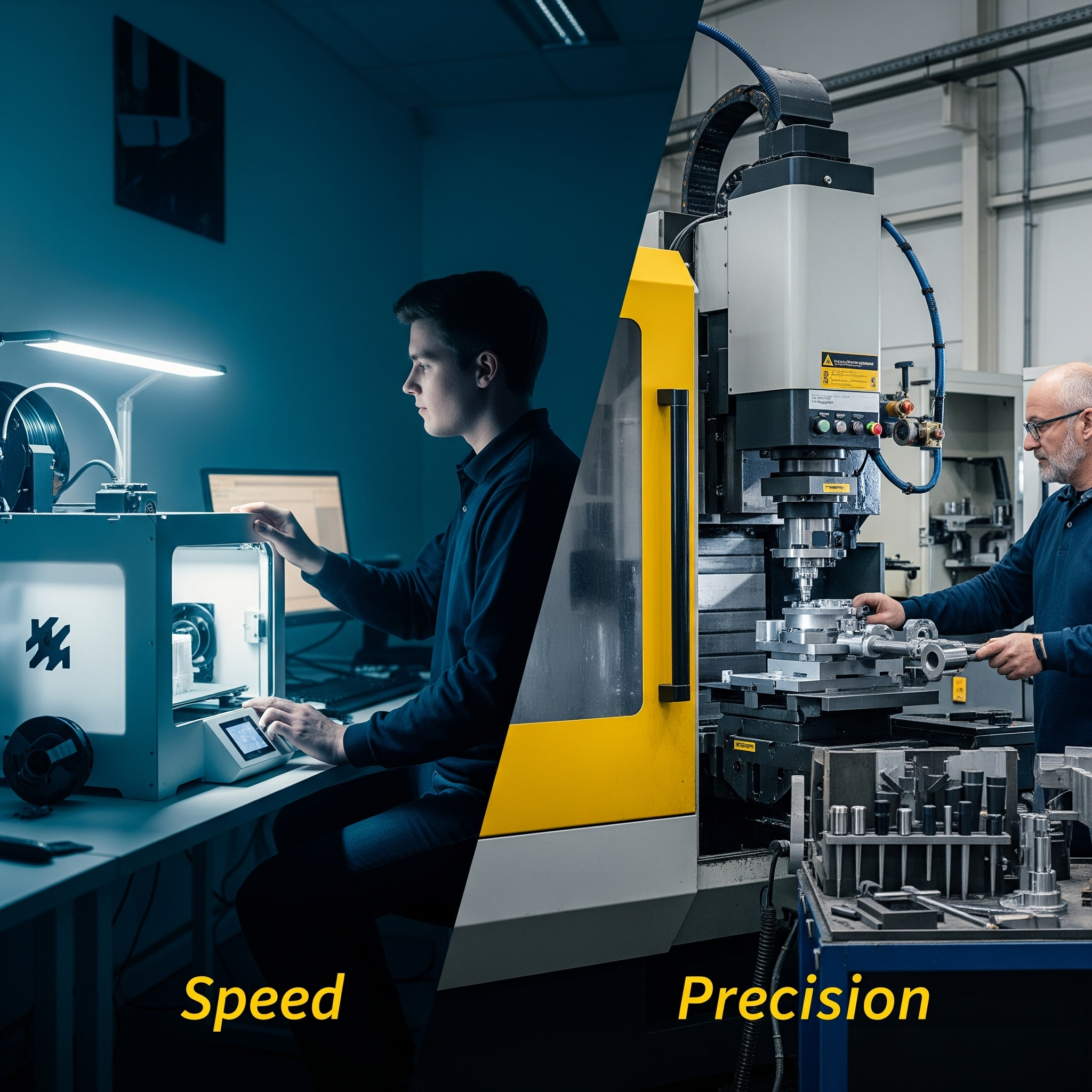
Rapid prototyping and production serve different goals. Prototyping optimizes for speed and learning; production optimizes for repeatability, cost, and quality at scale.
When to Pivot
Pivot when design is stable, requirements are validated, and the economics of tooling and process changes make sense for volume.
Process Differences
- Prototyping: 3D printing, soft tooling, quick-turn CNC, manual assembly.
- Production: hard tooling, injection molding, DFM/DFA, automation, quality systems.
Cost and Quality
Prototyping tolerates higher unit costs for speed; production drives cost down with tooling, fixtures, and optimized routing while enforcing tighter quality controls.
Team and Documentation
Shift to production with controlled BOMs, process docs, test plans, and supplier alignment to prevent surprises at scale.
 Warning
Warning